Know More About Stainless Steel Orthopaedic Implant

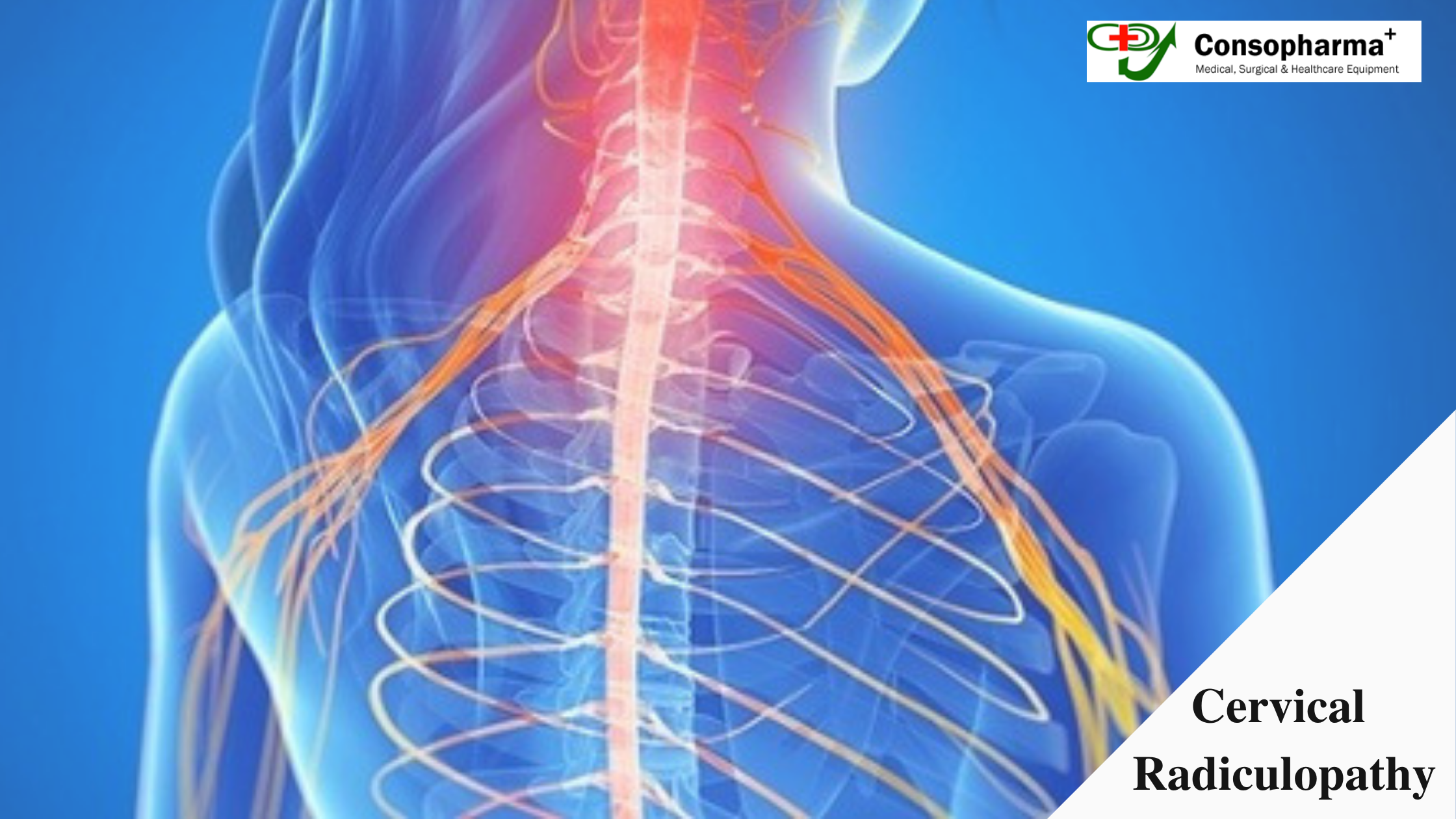
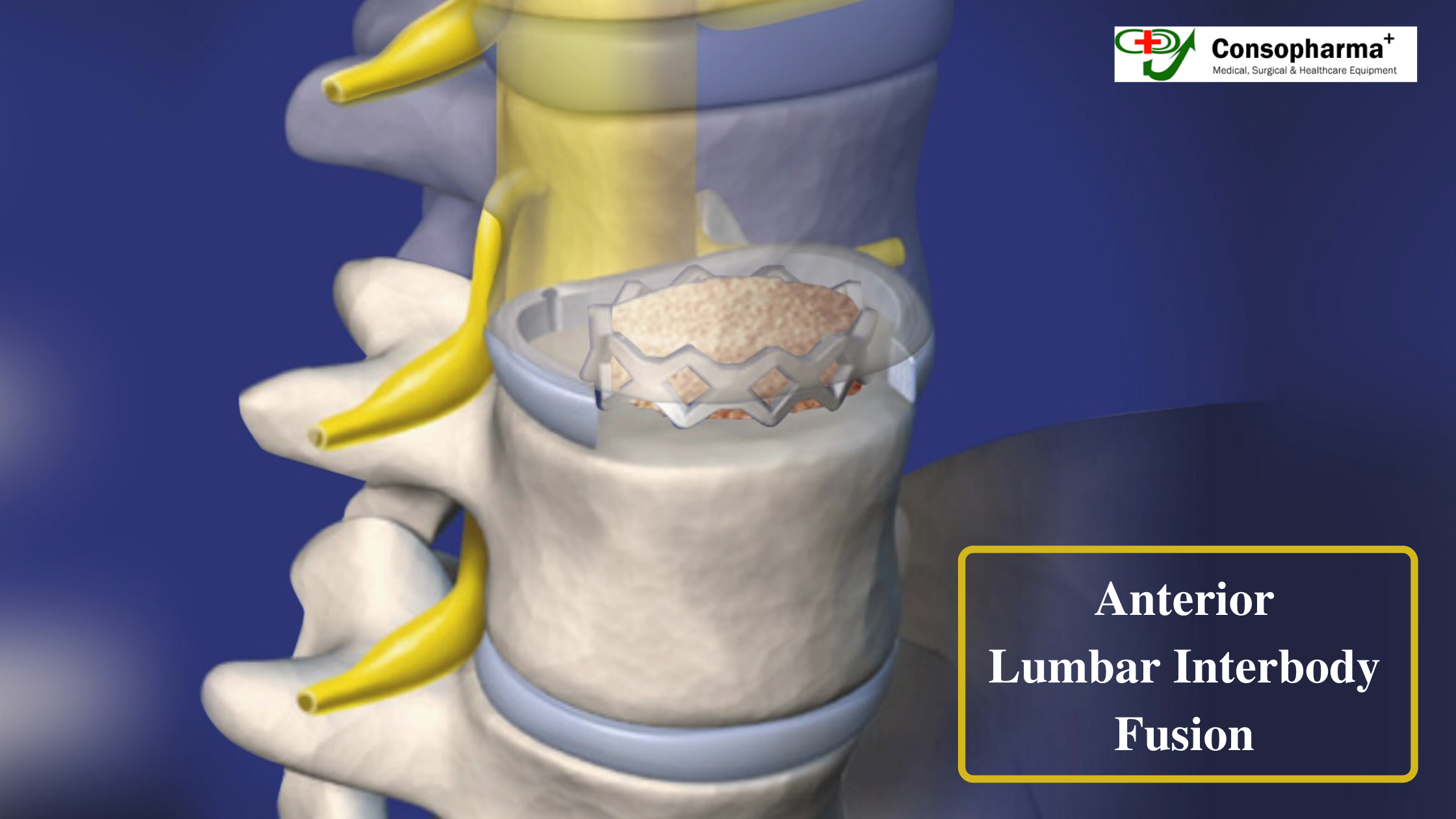
An orthopaedic implant is a medical device made to replace a joint that’s been worn out or to support a damaged bone. It requires a surgical procedure to put in place, and the durability varies based on its use. There are various orthopaedic instrument suppliers that provide best quality orthopaedic implants to the surgeons. Examples of orthopaedic implants are bone plates and screws used in spinal fusion surgery, and the implants used in hip and joint replacement surgery. Stainless steel is usually used for non-permanent implants because of its desirable structural properties, biocompatibility, and its load-bearing capability. The lifespan of stainless steel implants is usually divided into three categories, namely –
- Pre-vivo
- In-vivo
- Post-vivo
Pre-vivo:
The mechanical properties of stainless steel (specifically, 316L stainless steel) make it a good ‘biomaterial’ used in fixation implants. The pre-vivo stage of a stainless steel implant involves the manufacturing of the implant from 316L stainless steel. Multiple processes are used, but the most common are cold-working and forging, which gives the stainless steel different physical properties as required for the implant.
In-vivo:
The in-vivo stage of an implant is the period for which it is used as an implant. The implants must fit the anatomical or pathological requirements of the injured structure. Once implanted, it will either remain for the patient’s lifetime or can be removed.
Post-vivo:
In some cases, implant removal may be necessary. There are certain symptoms that may indicate the need for an implant removal procedure. In adults, local pain, soft tissue irritation, infection, or obstruction of ligaments or tendons are indicators of a possible need for implant removal. In children, it is recommended to remove the implant as soon as the healing process has completed. There are multiple methods of implant removal, depending on the location and need for removal. Implant removal is a common procedure in orthopaedic surgery. Once removed, the implant may be shipped to pathology and recycled, or donated to developing countries for secondary use.
Orthopaedic surgeons, with the help of orthopaedic surgical instruments treat a variety of orthopaedic conditions such as musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries and other structural weaknesses or breakages.